Stress is an inevitable part of life, affecting everyone at some point. While most people are aware of the general health consequences of stress, such as heart disease, high blood pressure, and mental health issues, fewer are aware of its impact on oral health. Chronic stress can lead to various dental problems, ranging from teeth grinding and gum disease to dry mouth and oral infections. Understanding the connection between stress and oral health is crucial for preventing these issues and maintaining a healthy smile. Let’s learn more about the impact of stress on oral health.
Table of Contents
Oral health problems that can arise from too much stress
Teeth Grinding (Bruxism)
One of the most common oral health issues linked to stress is bruxism, or teeth grinding. Stress and anxiety are significant contributors to this condition, often causing people to clench or grind their teeth, especially during sleep.
• Symptoms: Bruxism can lead to worn-down teeth, jaw pain, headaches, and even fractured teeth. Over time, this constant pressure can damage dental restorations, such as crowns and fillings, and cause temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders.
• Prevention and Treatment: To manage bruxism, stress reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and regular physical activity are essential. Dentists may recommend a custom-made nightguard to protect teeth during sleep in severe cases.
Gum Disease (Periodontitis)
Chronic stress can weaken the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections, including gum disease. Periodontitis is a severe form of gum disease that affects the gums and the bone supporting the teeth.
• How Stress Contributes: When stressed, the body produces more cortisol, a hormone that can lead to inflammation throughout the body, including the gums. This inflammation can exacerbate existing gum disease or increase the likelihood of developing it.
• Prevention and Treatment: Maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial for preventing gum disease, especially during stressful times. This includes brushing twice daily, flossing, and regular dental check-ups. Managing stress through healthy lifestyle choices, such as a balanced diet, exercise, and adequate sleep, can also help reduce the risk.
Dry Mouth (Xerostomia)
Stress is known to affect salivary flow, often leading to dry mouth or xerostomia. Saliva plays a critical role in oral health by neutralizing acids produced by bacteria, washing away food particles, and providing disease-fighting substances throughout the mouth.
• Consequences of Dry Mouth: Reduced saliva flow can increase the risk of cavities, bad breath, gum disease, and oral infections like thrush (a yeast infection).
• Prevention and Treatment: Staying hydrated, chewing sugar-free gum, and using saliva substitutes can help alleviate dry mouth symptoms. Reducing stress through mindfulness practices and staying hydrated are also important steps.
Canker Sores
Canker sores, or aphthous ulcers, are small, painful ulcers that can appear on the inside of the mouth. While the exact cause of canker sores is not fully understood, stress is considered a significant trigger.
• Symptoms: Canker sores are typically round or oval with a white or yellowish center and a red border. They can make eating, drinking, and talking uncomfortable.
• Prevention and Treatment: Managing stress is key to reducing the frequency and severity of canker sores. Avoiding spicy or acidic foods that can irritate sores and using over-the-counter topical treatments can help ease discomfort.
Weakened Immune Response and Oral Infections
Chronic stress can suppress the immune system, making the body more vulnerable to infections, including mouth infections. This can increase the risk of oral infections such as thrush, herpes simplex virus (cold sores), and periodontal infections.
• How Stress Affects Immunity: Prolonged stress can cause the body to produce fewer lymphocytes, white blood cells that help fight off infections. This weakened immune response can lead to more frequent or severe oral infections.
• Prevention and Treatment: Strengthening the immune system through a healthy diet rich in vitamins and minerals, adequate sleep, and regular exercise can help reduce the risk of infections. Stress management techniques such as yoga, meditation, and counselling can also be beneficial.
Neglect of Oral Hygiene
Stress can often lead to neglecting daily routines, including oral hygiene. When stressed, people may skip brushing and flossing, which can quickly lead to cavities, gum disease, and other dental problems.
• Impact: Poor oral hygiene due to stress can cause plaque build-up, leading to tooth decay and gum disease.
• Prevention: Maintaining a consistent oral hygiene routine is essential even during stressful times. Setting reminders and incorporating stress-relief activities into your day can help maintain this habit.
Managing Stress for Better Oral Health

Managing stress is essential for maintaining overall well-being and is crucial in preserving your oral health. Chronic stress can significantly affect your teeth and gums, leading to conditions such as bruxism, gum disease, dry mouth, and even neglect of daily oral hygiene routines. By focusing on stress management techniques tailored to support dental health, you can protect your smile and prevent long-term dental issues.
Incorporate Relaxation Into Your Day
Relaxation techniques are powerful tools for reducing stress levels and minimizing their impact on oral health. Practices like deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help lower cortisol levels, the stress hormone linked to inflammation and immune suppression.
• Deep Breathing Exercises: Taking a few minutes each day to practice deep breathing can help calm your nervous system. This reduction in stress can decrease the likelihood of bruxism (teeth grinding) and help maintain a healthy balance of saliva in your mouth, which is crucial for preventing dry mouth and tooth decay.
• Meditation: Regular meditation has been shown to reduce stress significantly. By practicing mindfulness, you can become more aware of your body’s reactions to stress, such as clenching your jaw or grinding your teeth, allowing you to address these issues before they cause damage.
• Yoga: Yoga combines physical activity with mindfulness, making it an excellent way to relieve stress. The physical postures, combined with focused breathing, can reduce muscle tension in the jaw and neck, areas often affected by stress-related bruxism.
Maintain a Balanced Diet
Your diet plays a vital role in managing stress and supporting oral health. Stress often leads to cravings for sugary or processed foods, which can harm your teeth and gums. A balanced diet rich in nutrients helps bolster your immune system and keep your oral health in check.
• Increase Intake of Antioxidants: Foods high in antioxidants, such as berries, leafy greens, and nuts, can help reduce inflammation in the gums. Stress-induced inflammation is a risk factor for gum disease, so eating antioxidant-rich foods can help mitigate this.
• Stay Hydrated: Stress can contribute to dry mouth, which increases the risk of cavities and bad breath. Drinking plenty of water helps maintain saliva production, which is essential for neutralizing acids and washing away food particles.
• Limit Sugary and Acidic Foods: Stress often leads to increased consumption of comfort foods, which are usually high in sugar and acid. These can erode enamel and contribute to cavities. Opt for healthier snacks like fruits, vegetables, and cheese, which protect your teeth and provide essential nutrients.
Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Physical activity is a proven stress reliever and has a positive impact on your oral health. Regular exercise can help reduce the physical symptoms of stress, such as muscle tension and jaw clenching, while also promoting overall health.
• Exercise Reduces Bruxism: Physical activity can reduce the frequency and intensity of teeth grinding by helping to release built-up tension. This is especially beneficial if you engage in activities that involve the entire body, such as running, swimming, or cycling.
• Improves Sleep Quality: Regular exercise also improves sleep quality, which is often disrupted by stress. Better sleep reduces nighttime bruxism risk and helps maintain oral health.
Prioritize Oral Hygiene
Stress can lead to neglect of daily routines, including oral hygiene. Maintaining a consistent oral care routine, especially during stressful periods, is crucial to prevent the onset of dental problems.
• Set Reminders: Use alarms or reminders to ensure you don’t skip brushing and flossing, even on the most stressful days. This helps prevent plaque build-up, which can lead to cavities and gum disease.
• Use Stress-Reducing Oral Care Products: Consider using toothpaste or mouthwash with stress-relieving scents like lavender or chamomile. These products can make your oral hygiene routine more enjoyable and help you relax.
• Practice Mindfulness: Turn your oral care routine into a mindful practice. Pay attention to the sensation of brushing and flossing, and take it as an opportunity to slow down and focus on your well-being.
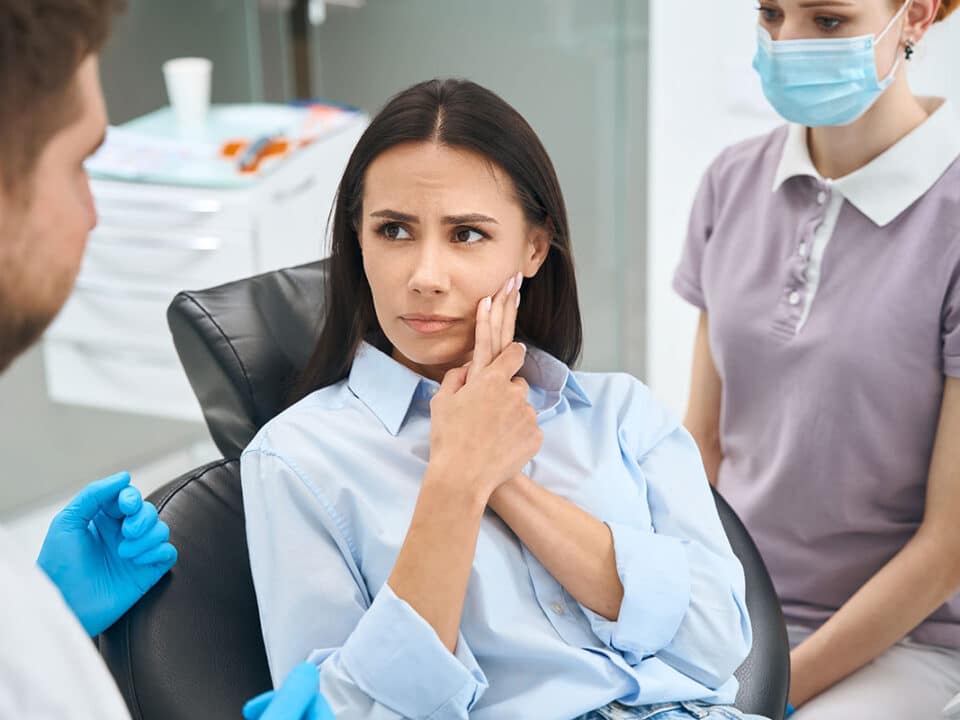
Visit Your Dentist Regularly and Communicate About Stress
Regular dental check-ups are essential for catching stress-related dental issues early. Your dentist can provide tailored advice on managing stress and its effects on your oral health.
Discuss Your Stress:
If you’re experiencing high levels of stress, let your dentist know. They can look for signs of stress-related conditions like bruxism or gum disease and suggest appropriate treatments.
• Custom-Made Nightguards: If you’re grinding your teeth due to stress, your dentist may recommend a custom-made nightguard. This device protects your teeth from wear and tear while you sleep, preventing long-term damage.
Follow-Up Care:
Follow-up care is essential if you’ve been treated for a stress-related dental issue. Regular visits will help monitor your progress and ensure your oral health remains stable.
Get Adequate Sleep to Support Oral Health
Stress often disrupts sleep, leading to a vicious cycle where lack of rest increases stress levels, harming oral health. Prioritizing sleep is crucial for managing stress and protecting your teeth and gums.
Establish a Bedtime Routine:
Create a calming bedtime routine that signals your body it’s time to sleep. This could include reading, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation techniques.
Avoid Stimulants:
Reduce your intake of caffeine and sugar, especially in the hours leading up to bedtime. These can disrupt sleep patterns and contribute to grinding teeth at night.
Sleep Position:
If you’re prone to bruxism, consider sleeping on your back. This position reduces pressure on the jaw and can decrease the likelihood of grinding your teeth.
How your dentist can help you manage stress-related oral health problems
How Your Dentist Can Help

Identifying Stress-Related Oral Health Issues
Dentists are often the first to notice the signs of stress-related oral health problems, such as teeth grinding (bruxism), gum disease, or canker sores. By conducting thorough examinations and asking about symptoms like jaw pain, headaches, or gum irritation, a dentist can identify these issues early and take steps to address them before they worsen. Your dentist can also help identify other issues that might be linking your dental health to your overall health.
Providing Custom-Made Nightguards
Dentists can create custom-made nightguards for patients who grind their teeth at night due to stress. These devices protect the teeth from excessive wear, prevent fractures, and reduce the strain on the jaw muscles. Wearing a nightguard can significantly alleviate the symptoms associated with bruxism, such as jaw pain and headaches, and protect the teeth from long-term damage.
Offering Stress-Relief Techniques
Dentists can offer advice on stress-relief techniques that can help reduce the impact of stress on oral health. This could include topics like relaxation techniques or dietary advice.
Educating Patients About the Effects of Stress on Oral Health
Education is key to prevention. Dentists can inform patients about how stress affects their oral health and the importance of maintaining good oral hygiene during stressful periods. This includes brushing and flossing regularly, staying hydrated, and avoiding habits that can exacerbate stress-related oral health issues, such as nail-biting or chewing on hard objects.
Monitoring and Managing Gum Disease
Since stress can weaken the immune system and exacerbate gum disease, dentists can provide specialized care to help manage and treat gum conditions. This might include more frequent cleanings, scaling and root planing, or prescribing antimicrobial mouthwashes to help control the bacteria that contribute to gum disease.
Personalized Care Plans
Dentists can develop personalized care plans that consider the patient’s stress levels and their impact on oral health. These plans might include more frequent check-ups, tailored advice on stress management, and specific treatments aimed at mitigating the effects of stress on the mouth and gums.
Referrals to Other Health Professionals
When stress significantly impacts oral health, dentists can consult with patients about seeking help from other healthcare professionals, such as psychologists or stress management specialists. This interdisciplinary approach ensures that patients receive comprehensive care that addresses both the physical and emotional aspects of stress.
Providing Support and Reassurance
Finally, simply offering support and reassurance can make a big difference. Dentists can create a calm and relaxing environment in their practice, which can help reduce anxiety and stress for their patients. This supportive atmosphere encourages patients to discuss their stress and its impact on their health, allowing the dentist to provide more effective care.
Conclusion
Stress can significantly impact your oral health, leading to a range of issues from teeth grinding to gum disease. By understanding the connection between stress and oral health, you can take proactive steps to protect your teeth and gums. Implementing stress management techniques, maintaining a consistent oral hygiene routine, and seeking regular dental care are essential strategies for preserving your oral health in the face of stress. If you’re experiencing stress-related dental issues, don’t hesitate to discuss them with your dentist—they can provide tailored advice and treatment options to help you maintain a healthy smile.
Check us out on Facebook and Twitter for daily information about Oral Health from Martindale Dental, or visit our offices in Hamilton and St. Catharines.
Have more questions?
Please contact us for all inquiries or to book an appointment with one of our convenient clinic locations. We look forward to hearing from you.