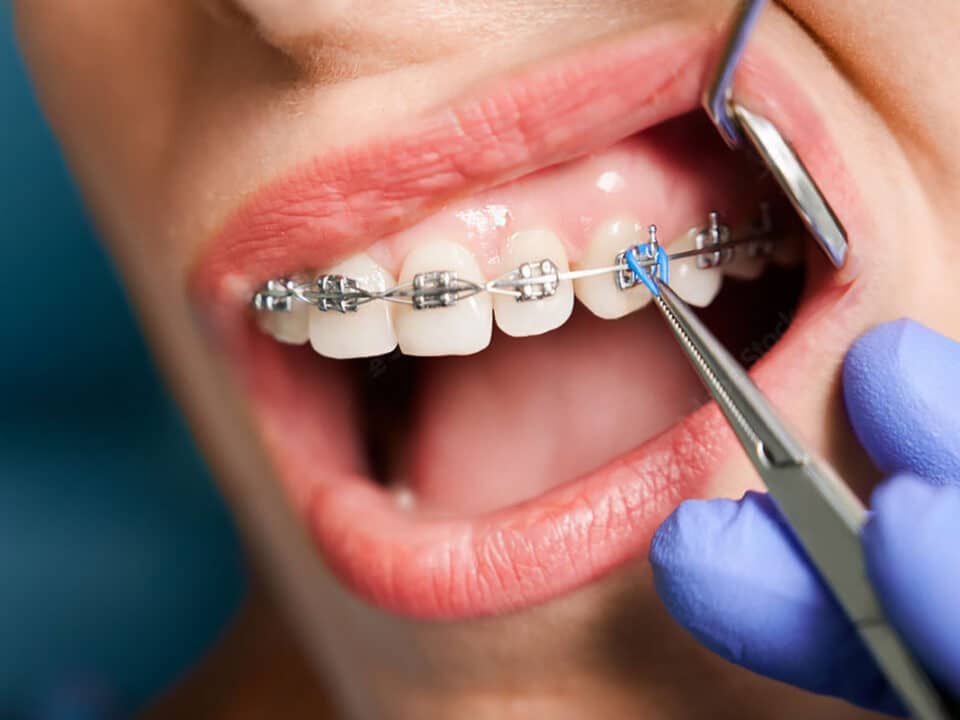
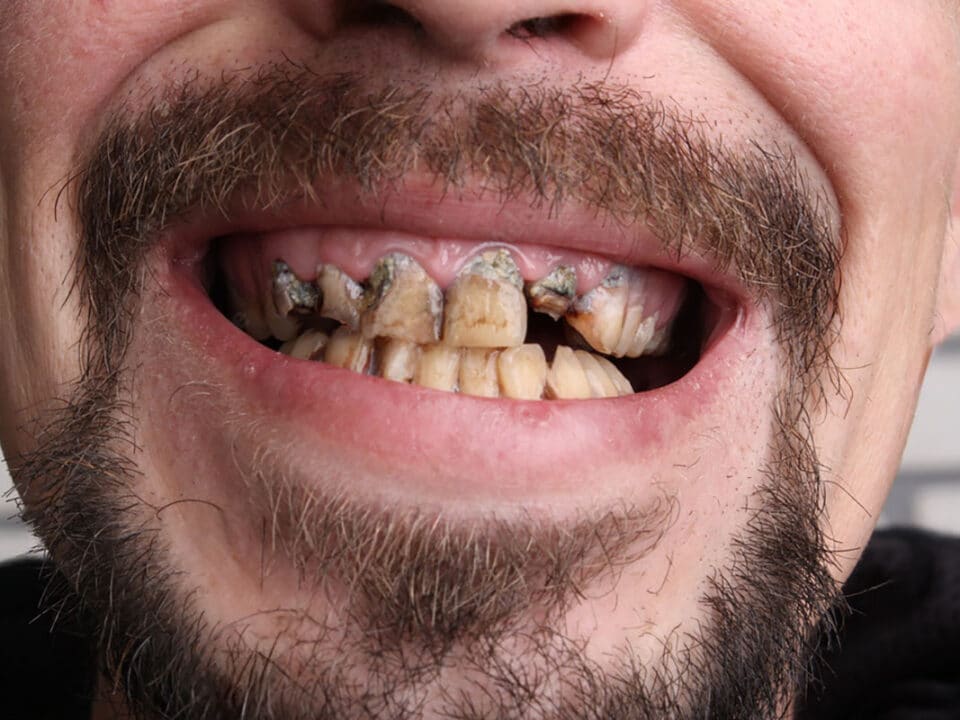
Gum recession is a common dental issue that can cause both cosmetic and functional problems. Many people wonder can gum recession be reversed or if they are destined to live with it once it starts. While true gum regeneration is limited, there are ways to halt the progression, treat the symptoms, and even partially restore the gum line. This comprehensive article will explore the causes of gum recession, preventive measures, and various treatment options, including the potential for reversing gum loss.
Table of Contents
Understanding Gum Recession
Gum recession occurs when the gum tissue surrounding the teeth pulls back or wears away, exposing more of the tooth or its root. This condition can result in increased tooth sensitivity, a higher risk of decay, and an undesirable aesthetic appearance. Left untreated, gum recession can lead to serious dental issues, including tooth loss.
Causes of Gum Recession
Several factors can contribute to gum recession:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: When plaque and tartar build-up on the teeth due to inadequate brushing and flossing, they can irritate the gums, causing inflammation and eventual recession. Chronic inflammation, known as gingivitis, can progress to periodontitis, significantly contributing to gum loss.
- Aggressive Brushing: Brushing too hard or using a toothbrush with stiff bristles can erode the delicate gum tissue over time. It also works to irritate gums, causing them to become inflamed. If this inflammation lingers, then gums will begin to recede. Many believe vigorous brushing results in cleaner teeth, but it can wear down both enamel and gum tissue, leading to recession.
- Periodontal Disease: One of the most common causes of gum recession. Periodontal disease results from bacterial infections that destroy gum tissue and supporting bone structures. As the disease progresses, the gums pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that deepen over time.
- Genetics: Research indicates that some individuals are genetically predisposed to gum recession. People with naturally thin or fragile gums are more susceptible to recession, even with good oral hygiene practices.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause can make gums more sensitive and prone to recession. Elevated hormone levels can increase blood flow to the gums, making them more reactive to plaque and bacteria.
- Tobacco Use: Smoking or chewing tobacco reduces blood flow to the gums, impairing the healing process and promoting inflammation. Additionally, tobacco users tend to have more plaque buildup, which exacerbates gum recession.
- Misaligned Teeth or Bite Issues: Malocclusion, misaligned teeth, and other orthodontic disorders can place uneven pressure on the gums during chewing. Over time, this uneven pressure can cause the gums to recede in areas that experience excessive force.
- Grinding and Clenching: Bruxism or teeth grinding places excessive force on the teeth and supporting structures. This constant pressure can wear down the gum tissue and lead to recession, especially if bruxism occurs at night.
- Piercings: Oral piercings, such as lip or tongue, can repeatedly rub against the gums, causing irritation and tissue damage. Over time, this irritation can result in gum recession at the contact points.
Can Gum Recession Be Reversed?
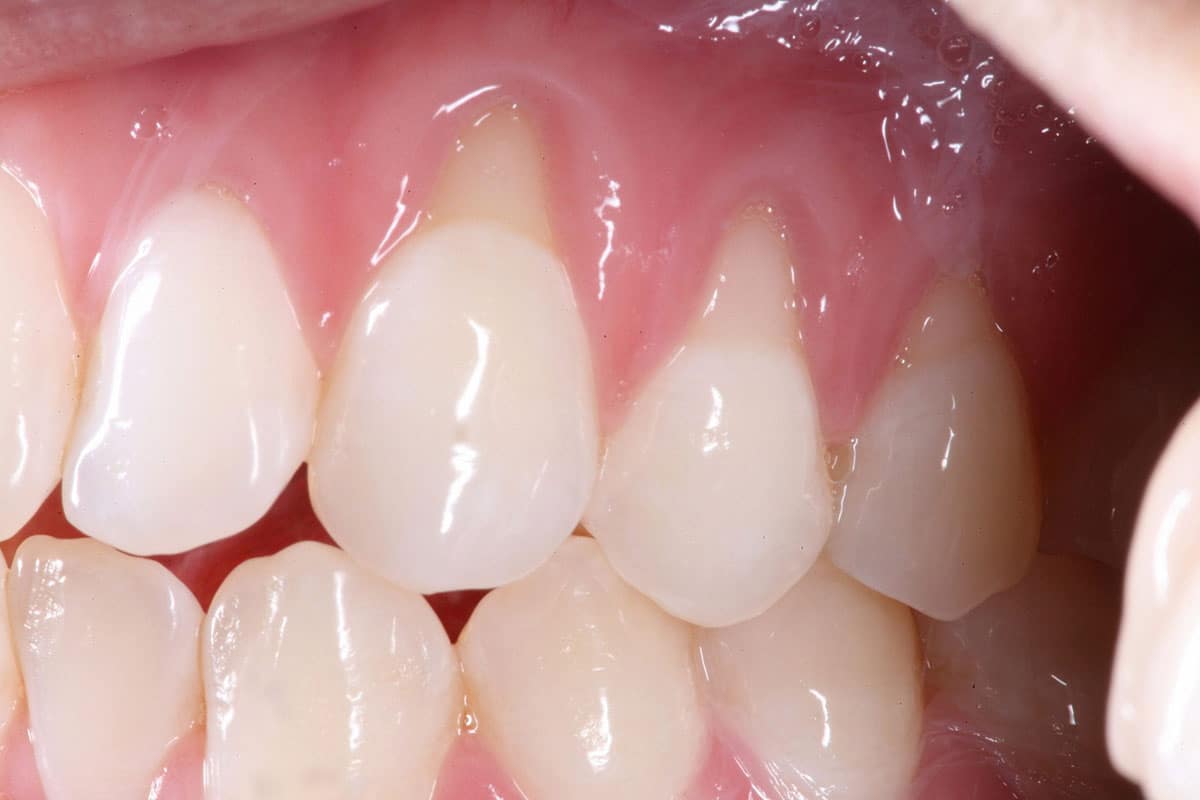
The short answer is that while lost gum tissue cannot regenerate independently, several effective ways exist to treat and manage gum recession. These treatments can help restore the appearance of the gums, protect the teeth, and prevent further recession.
Reversing gum recession depends on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. In mild cases, addressing the cause and improving oral hygiene can lead to significant improvement. In more advanced cases, professional treatments, including surgical procedures, may be necessary to restore the gum line.
Mild Gum Recession
For mild cases of gum recession, early intervention can help stop the progression and improve the appearance of the gums. Key strategies include:
Adopting Proper Oral Hygiene Practices: Switching to a soft-bristled toothbrush and gently brushing techniques can prevent further damage. Regular flossing and using an antiseptic mouthwash can reduce plaque and bacteria buildup.
Reducing Risk Factors: Avoiding habits that contribute to gum recession, such as smoking, aggressive brushing, or using abrasive toothpaste, can help preserve gum tissue.
Using Desensitizing Products: Special toothpaste or gels designed for sensitive teeth can help manage symptoms associated with exposed tooth roots.
Moderate Gum Recession
When gum recession has progressed beyond the mild stage but is not severe enough to require surgery, professional treatments can help manage the condition. These include:
Scaling and Root Planing: A deep cleaning procedure that removes plaque and tartar below the gum line. Smoothing the root surfaces helps the gums reattach to the teeth and reduces further recession.
Antibiotic Therapy: If a bacterial infection is present, antibiotics can be applied topically or taken orally to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
Laser Therapy: Some dental professionals use laser treatments to remove infected tissue and stimulate the regeneration of healthy gum tissue.
Severe Gum Recession
In cases of severe gum recession, surgical intervention is often required to restore the gum line and protect the tooth roots. The primary goal of these procedures is to cover exposed roots, reduce sensitivity, and improve the overall aesthetics of the smile.
Gum Grafting
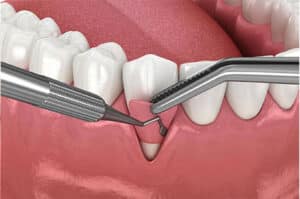
This involves transplanting tissue from the roof of the mouth or a donor source to the affected area. The grafted tissue is stitched into place, promoting new tissue growth and restoring the gum line.
There are several types of gum grafts:
Connective Tissue Grafts: A flap of skin is cut at the roof of the mouth, and the tissue beneath is removed and stitched to the affected area.
Free Gingival Grafts: Tissue is directly taken from the roof of the mouth and attached to the receded gums.
Pedicle Grafts: Tissue is partially cut from an adjacent area and rotated over the exposed root.
Gum grafting not only improves the appearance of the gum line but also helps protect the tooth roots from decay and sensitivity.
Pinhole Surgical Technique (PST)
A minimally invasive procedure where a small hole is made in the gum and special instruments are used to loosen and reposition the gum tissue over the exposed roots. PST has a faster recovery time than traditional grafting and does not require donor tissue.
Guided Tissue Regeneration
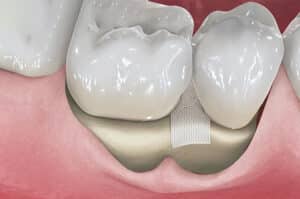
This involves placing a membrane between the gum and bone to encourage the regrowth of bone and gum tissue. If significant bone loss is present, this procedure is often combined with bone grafting.
Tissue-Stimulating Proteins
Applying enamel matrix derivative proteins can promote tissue regrowth and attachment, helping regenerate gum tissue and reduce pocket depth.
Managing Expectations
It’s important to note that while these treatments can restore the appearance of the gums and protect the teeth, complete regrowth of lost gum tissue is rare. Treatment aims to manage symptoms, prevent recession, and improve oral health.
Preventing Gum Recession

Since your gums cannot grow back once they’ve receded, prevention becomes the most important thing you can do.
By following these preventive measures, you can reduce the risk of gum recession or stop it from progressing:
Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
- Brush twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Use a gentle technique, focusing on cleaning along the gum line without applying too much pressure.
- Floss daily to remove plaque from between the teeth and below the gum line. Regular flossing helps prevent the buildup of plaque that can lead to gum irritation.
- Consider using interdental brushes or a water flosser for more effective cleaning, especially if you have gaps between your teeth.
Use Proper Brushing Techniques
- Avoid aggressive brushing; use gentle, circular motions rather than back-and-forth scrubbing.
- Consider using an electric toothbrush with a pressure sensor to prevent over-brushing and ensure thorough yet gentle cleaning.
- Replace your toothbrush every three to four months or sooner if the bristles are frayed.
Visit the Dentist Regularly
- Schedule dental checkups and cleanings at least twice a year. Professional cleanings remove plaque and tartar that cannot be removed by regular brushing and flossing.
- Your dentist can monitor your gum health and identify early signs of recession or gum disease, allowing prompt intervention.
Address Bruxism
- Talk to your dentist about a custom-made night guard if you grind or clench your teeth. Night guards can protect your teeth and gums from the excessive force caused by grinding.
- Stress management techniques, such as meditation or exercise, can also help reduce bruxism caused by stress.
Quit Tobacco Use
- Tobacco use is a significant risk factor for gum disease and recession. Quitting smoking or using other tobacco products can significantly improve gum health.
- Seek support from cessation programs, counselling, or medications if needed.
Correct Bite Issues
- If you have misaligned teeth or an improper bite, orthodontic treatment can help distribute chewing forces evenly, reducing the risk of recess.
- Consult an orthodontist to explore options such as braces or clear aligners.
Avoid Gum Irritants
- If you have oral piercings, be mindful of the potential for gum irritation and recession. Consider removing piercings that frequently come into contact with your gums.
- Avoid using abrasive toothpaste or harsh mouth rinses that can irritate the gum tissue.
Maintain a Balanced Diet
- A diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin C and calcium, supports healthy gums. Vitamin C helps in collagen production, which is essential for gum strength, while calcium supports bone and tooth health.
- Stay hydrated to promote saliva production, which helps neutralize acids and wash away bacteria.
Use Antibacterial Mouthwash
- An antibacterial mouthwash can help control plaque and reduce gum inflammation.
- Look for mouthwashes containing chlorhexidine or essential oils for added gum protection.
Be Mindful of Changes in Your Gums
- Regularly inspect your gums for changes, such as increased sensitivity, swelling, or receding areas. Early detection of gum issues can lead to more effective treatment.
We also have an article dedicated to minimizing gum damage, which can be found here.
Final Thoughts
While gum recession cannot be fully reversed without surgical intervention, many effective treatments can manage the condition, restore gum health, and improve the appearance of your smile. By adopting good oral hygiene habits, addressing underlying causes, and seeking professional treatment when necessary, you can protect your gums and teeth for years to come.
If you suspect you have gum recession, consult your dentist or periodontist for an evaluation. Early intervention can prevent more severe issues and help you maintain a healthy, confident smile
Early signs include tooth sensitivity, visibly longer teeth, notches near the gum line, and inflamed or tender gums.
Yes, it is a common dental problem, especially among adults over 30 years old.
If left untreated, severe gum recession can cause tooth instability and eventually lead to tooth loss.
Yes, gum recession can contribute to bad breath due to the accumulation of bacteria in pockets around the teeth.
Gum recession itself may not be painful, but it can cause sensitivity to hot, cold, and sweet stimuli due to exposed tooth roots.
It can be. Periodontal disease is a leading cause of gum recession.
Treatment duration varies depending on the severity and the chosen intervention. Non-surgical treatments may take a few weeks, while surgical treatments can require a longer recovery period.
It’s recommended to visit the dentist at least twice a year for checkups and professional cleanings.
Check us out on Facebook and Twitter for daily information about Oral Health from Martindale Dental, or visit our offices in Hamilton and St. Catharines.
Have more questions?
Please contact us for all inquiries or to book an appointment with one of our convenient clinic locations. We look forward to hearing from you.